for 4 year exp
1. How would you troubleshoot a custom formula field that is not displaying the expected result?
Answer:
- Check if the formula syntax is correct.
- Ensure referenced fields are populated and accessible (field-level security, visibility in page layout).
- Verify data types (text vs number vs date mismatches).
- Check parent-child relationships if cross-object formula is used.
- Confirm user profile/permissions allow visibility of the field.
- Use “Check Syntax” in formula editor and test with sample data.
2. How many lookup relationship fields can we create on a single object?
Answer:
- A Salesforce object can have up to 40 relationship fields in total.
- Master-Detail: Maximum 2 per object.
- Lookup: The rest can be lookup (up to 38 if no master-detail).
3. What is the use of a Muting Permission Set in a Permission Set Group?
Answer:
A Muting Permission Set removes specific permissions from a Permission Set Group without changing the underlying permission sets.
Use case: You have a group that grants many permissions, but for certain users, you want to mute (disable) some of them.
4. Difference between Dynamic Dashboard and Static Dashboard?
Answer:
- Static Dashboard: Runs in the context of the dashboard creator → all users see the same data.
- Dynamic Dashboard: Runs in the context of the logged-in user → each user sees data according to their access.
5. What are the default filters available in Salesforce?
Answer:
In reports, default filters are:
- Created Date
- Last Modified Date
- Owner (My records, My team’s records, All records).
6. A user cannot see a custom object tab, even though they have the correct profile. What could be wrong?
Answer:
- Tab visibility is set to “Tab Hidden” in the profile.
- The object is not added to the App the user is using.
- User may lack object-level permission (Read/Create).
7. Difference between Custom Setting, Named Credential, and Connected App?
Answer:
- Custom Setting: Store app data/config values accessible in Apex without SOQL. Two types: List & Hierarchy.
- Named Credential: Securely store authentication details for external system callouts.
- Connected App: Allow external apps to connect to Salesforce using OAuth, manage authentication and permissions.
8. Difference between Interface and Abstract Class in Apex?
Answer:
- Abstract Class: Can have both defined and abstract methods, can define variables, can provide partial implementation.
- Interface: Only method signatures (no implementation), a class must implement all methods.
9. Limitations of Queueable Apex?
Answer:
- Cannot call another Queueable class directly inside (only one additional enqueueJob is allowed).
- Cannot be called from Batch Apex or Scheduled Apex.
- Limited to async context and governor limits still apply.
10. Can we call a Future Method from a Batch Class?
Answer:
No. Inside execute method: Not allowed. Salesforce prevents calling another async process (Future, Queueable, Batch, or Schedulable) inside a running batch’s execute. Inside finish method: Allowed.
11. Difference between Database.QueryLocator and Iterable in Batch Apex?
Answer:
- Database.QueryLocator:
- Returns up to 50 million records.
- Best for simple queries.
- Iterable:
- Returns only 50,000 records.
- Used when you need to pass a complex/custom collection.
12. SOQL 101 error during deployment – what is the cause?
Answer:
- It occurs when more than 100 SOQL queries are executed in a single transaction.
- Typically caused by placing SOQL inside a loop.
Fix: Bulkify code → move queries outside loops, use collections & maps.
13. Business wants to change batch size dynamically – how do you achieve this?
Answer:
- Store batch size in Custom Setting or Custom Metadata.
- Fetch value in Apex, pass it to
Database.executeBatch(batchClass, batchSize);
14. How to handle recursive triggers?
Answer:
- Use a static Boolean flag or static Set/Map to prevent re-entry.
- Or use a Trigger Framework to handle recursion properly.
15. How to handle recursive triggers?
Answer:
- Use a static Boolean flag or static Set/Map to prevent re-entry.
- Or use a Trigger Framework to handle recursion properly.\
16. What is a Custom Event in LWC?
Answer:
- A Custom Event allows communication between components.
- Typically used for child-to-parent communication.
Example: A child component dispatchesthis.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent('myevent', { detail: data }));which the parent listens to.
18. SOQL Query: Get Accounts with more than 10 Contacts
Answer:
SELECT Id, Name FROM Account WHERE Id IN ( SELECT AccountId FROM Contact GROUP BY AccountId HAVING COUNT(Id) > 10 )19. Trigger: Update Account with number of Contacts whenever Contact is inserted/updated/deleted/undeleted
trigger ContactTrigger on Contact (after insert, after update, after delete, after undelete) {
Set
if(Trigger.isInsert || Trigger.isUpdate || Trigger.isUndelete) {
for(Contact c : Trigger.new) {
if(c.AccountId != null) accountIds.add(c.AccountId);
}
}
if(Trigger.isDelete) {
for(Contact c : Trigger.old) {
if(c.AccountId != null) accountIds.add(c.AccountId);
}
}
List
for(Account acc : [
SELECT Id, (SELECT Id FROM Contacts)
FROM Account
WHERE Id IN :accountIds
]) {
acc.Total_Contacts__c = acc.Contacts.size();
accountsToUpdate.add(acc);
}
if(!accountsToUpdate.isEmpty()) {
update accountsToUpdate;
}
}
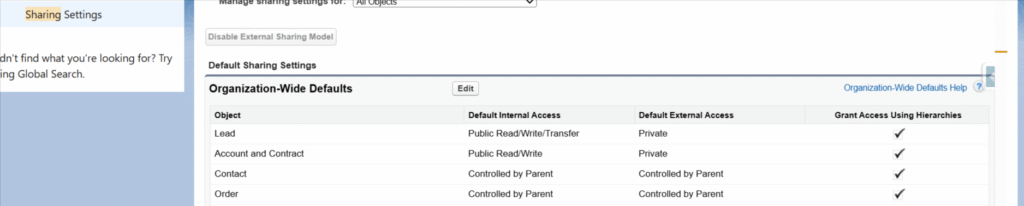
20. How to disable Role hierarchy in salesforce?
Answer:
In setup-> sharing setting -> Organization-Wide Defaults -> edit -> Checkbox for disable Grant Access Using Hierarchies
21. How to pass list in future method in salesforce?
Answer:
Before calling the future method, convert your List<sObject> (or other complex list) into a JSON string using JSON.serialize().
List
String accountsJson = JSON.serialize(accountsToProcess);
public class MyFutureMethods {
@future
public static void processAccountsAsync(String accountsJsonString) {
List
// Now you can work with the ‘accounts’ list
for (Account acc : accounts) {
System.debug(‘Processing Account: ‘ + acc.Name);
// Perform your asynchronous logic here
}
}
}

